Prokaryotic life forms. Morphology of eukaryotic cells. Cell organelles, their structure and functions. Cell membranes. Transport of substances through the cytoplasmic membrane.
Медицинская академия имени С.И. Георгиевского
ФГАОУ ВО «КФУ им. В.И. Вернадского»
Workbook
« В iology» of the student of 1 course
International Medical Faculty
Group ____
(Full Name)
Teacher ____________________________
Simferopol
2019
The calendar-thematic plan for practical class in biology
for students of the specialty " General Medicine" for 1 semester
Academic year.
| № | Topic |
| 1. | Levels of organization of the living. Cellular and non-cellular forms of life. Optical systems in biological research. |
| 2. | Prokaryotic life forms. Morphology of eukaryotic cells. Cell organelles, their structure and functions. Cell membranes. Transport of substances through the cytoplasmic membrane. |
| 3. | Characterization of nucleic acids: DNA, RNA. Replication. Repair. Genetic code and its properties. |
| 4. | Organization of the flow of information in the cell. Protein biosynthesis: transcription, translation. The structure of the pro- and eukaryotic gene. Genes are structural, regulatory. Regulation of gene expression. Molecular mechanisms of variation in humans. |
| 5. | Morphology of chromosomes. Karyotype of a Human. Methods for the study of chromosomes. The importance of studying the karyotype in medicine. |
| 6. | The life cycle of the cell. Cell division. Mitosis. Meiosis. Amitosis. Endomitosis. |
| 7. | Biological features of human reproduction. Gametogenesis. Fertilization. |
| 8. | Features of the prenatal period of human development. The background of congenital disorders. |
| 9. | Postnatal period of ontogenesis, regeneration, transplantation. |
| 10. | Features of human genetics. The manifestation of the basic laws of inheritance on the example of the man’s characterizing features of a person (mono-, di- and polyhybrid crossbreeding) Multiple allelism. Genetics of blood groups. |
| 11. | The interaction of allelic and non-allelic genes. The phenomenon of pleiotropy. |
| 12. | Linked inheritance. Crossingover. Genetics of the floor. Features of the inheritance of traits linked to the floor. |
| 13. | Variability, its forms and manifestations. The molecular mechanism of variation in humans. |
| 14. | Hereditary diseases, their classification. |
| 15. | The basics of medical genetics. Cytogenetic, biochemical, genealogical diagnostic methods. PCR and DNA diagnostics. Population-statistical and twin diagnostic methods. Medical genetic counseling. Prenatal diagnosis. |
| 16. | The final class in cytology and genetics. |
|
|
|
Date: Practical class №1
Levels of organization of the living. Cellular and non-cellular forms of life. Optical systems in biological research.
Prepare answers to questions:
1. Biology as a science. Its tasks, objects, research methods.
2. Features of biology in the twenty-first century.
3. The importance of biology in the system of training a doctor.
4. The scientific definition of the essence of life. Properties of the living.
5. Levels of organization of the living. Give examples.
6. The cell as a historically established living system.
7. Cellular and non-cellular life forms. The modern definition of viruses. Morphology and ultrastructure of viruses.
8. Constructive parts of a light microscope.
9. Rules for working with a light microscope.
10. What is the resolution of a microscope? What is the limited resolution of a light microscope?
11. General idea of electron microscopy.
12. Stages of manufacturing a temporary micropreparation.
13. The use of biological research methods in modern medicine.
Practical assignments:
1. Denote the structure of the virus.
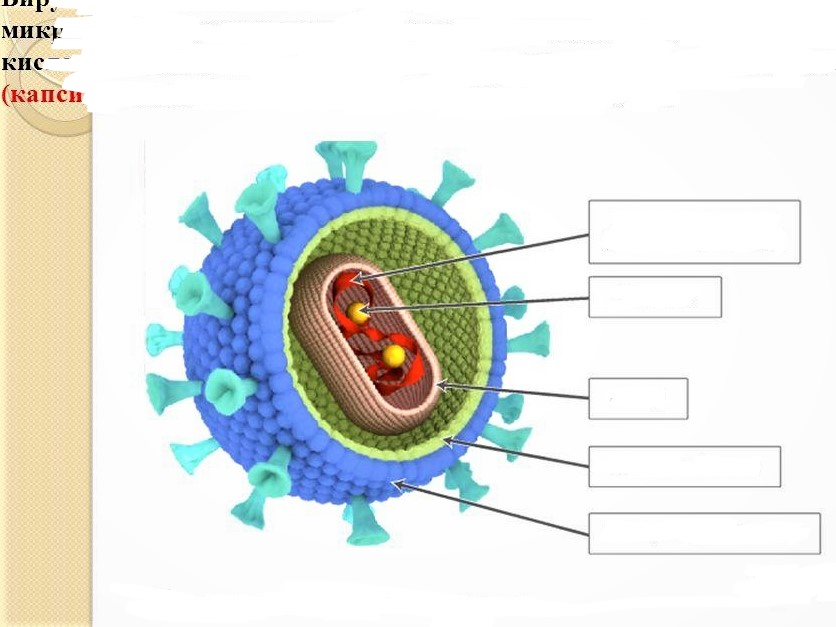
Structure of the virus: enzymes, capsid, protein membrane, nucleic acid, lipoprotein membrane.
2. Designate the structure of the bacterial cell.
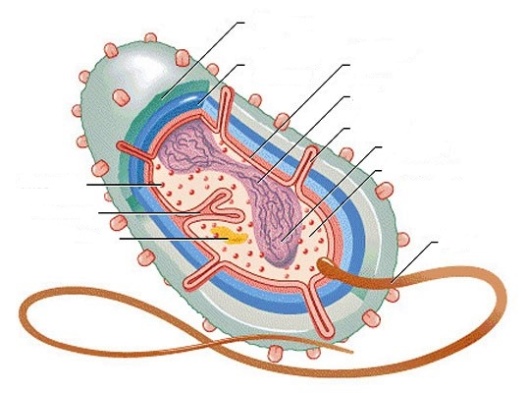
The structure of the bacterial cell: cytoplasm, ribosome, mesosome, capsule, plasmid, cell membrane, cytoplasmic membrane, DNA, fimbria, nucleoid, tourniquet.
3. Identify the elements of the picture, taking into account the dimensions of the human erythrocyte, bacterial
cell and various viruses.
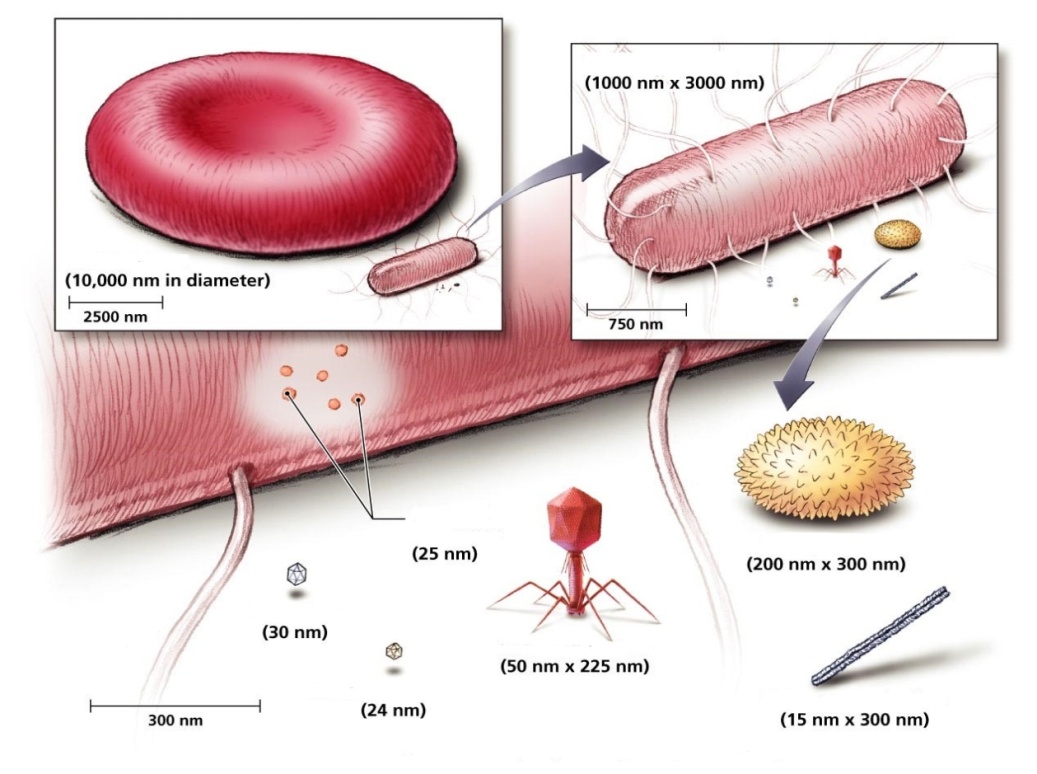
The figure shows: human erythrocyte, E. coli (Escherichia coli), bacterial ribosomes, poliovirus or poliomyelitis virus (Enterovirus C), bacteriophage MS2, bacteriophage T4, virus of natural or black smallpox (Variola vera), tobacco mosaic virus (Tobacco mosaic virus).
|
|
|
4. Designate a light microscope device.

Light microscope device: eyepiece, tube, macro-screw, micro-screw, base, tripod, mirror, condenser, condenser lift screw, stage, lenses, revolver.
5. Consider the asymmetric letter of the font under a small increase in the microscope.
Conclusion:______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
6. To examine and draw a microslide "Human Hair" under "small" and "large" magnification.
Small magnification Large magnification Conclusion:______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
7. To make a temporary slide of cotton fibers, consider under a microscope with small and large magnification. Draw, in the picture note artifacts in the form of debris and air bubbles.
Small magnification Large magnification Conclusion:______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Teacher's signature ______________________________________
Date: Practical lesson №2
|
|
|
Prokaryotic life forms. Morphology of eukaryotic cells. Cell organelles, their structure and functions. Cell membranes. Transport of substances through the cytoplasmic membrane.
Questions to prepare for the topic:
1. Structure of the eukaryotic cell.
2. Cytoplasm and its components: hyaloplasm, organoids, inclusions.
3. Classification of cytoplasmic organoids.
4. Organoids of general use.
5. Structure and function of single-membrane organelles: EPS, Golgi complex, lysosomes (species), peroxisomes, vacuoles of plant cells.
6. Structure and function of two-membrane organoids: mitochondria, plastids (chloroplasts, chromoplasts, leukoplasts).
7. Structure and function of non-membrane organoids: ribosomes, cell center, microtubules.
8. Organoids of special purpose: microvilli, cilia, flagella, myofibrils, neurofibrils.
9. Inclusions: trophic, secretory, special.
10. Organization of flows of substances, energy and information in the cell.
11. History of the development of ideas about the structure of the cell membrane.
12. Molecular organization of the biological membrane (models of Danieli and Dawson, Lenard (mosaic)).
13. Modern liquid-mosaic model of the structure of the biological membrane of Singer-Nicholson.
14. Chemical composition of the plasma membrane.
15. Functions of the membrane.
16. Passive transport of substances through the membrane: osmosis, simple diffusion, light diffusion.
17. Human erythrocytes in iso-, hypo- and hypertonic solutions.
18. Active transport. Principle of operation of sodium-potassium pump.
19. Endocytosis. Stages of phagocytosis. Pinocytosis.
20. Exocytosis.
1. Consider a microslide " Cuticula of Onion" with small and large magnification.
Draw and designate the structure of plant cells.
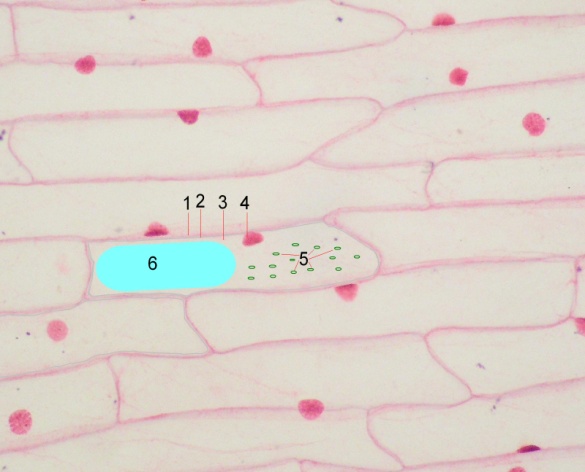
| 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- |
Large magnification
2. To consider the micropreparation "Frog Erythrocytes" with small and large magnification. Draw and designate the structure of the animal cell.
|
|
|
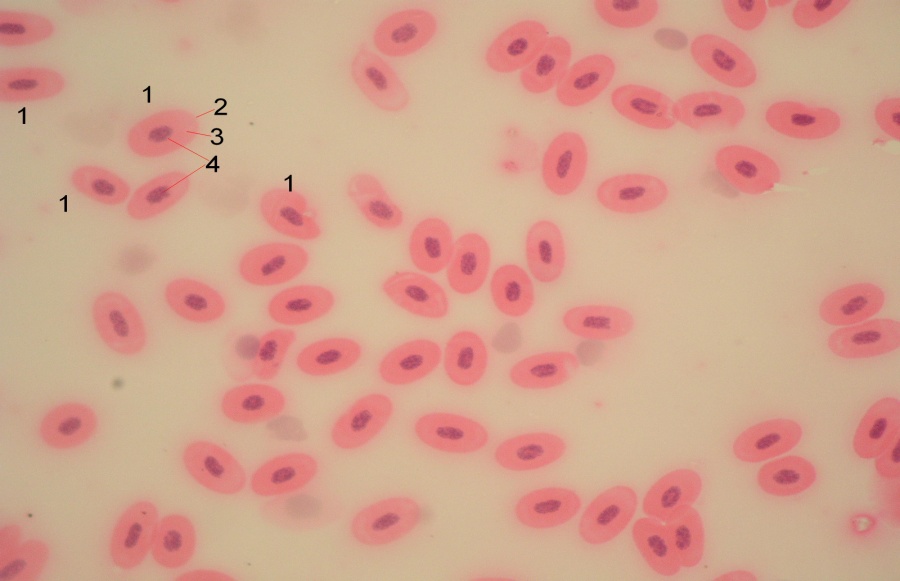
| 1- 2- 3- 4- |
Large magnification
3. Consider the microslide "Human Erythrocytes" with small and large magnification. Draw and denote the structure of an animal denuclearized cell.
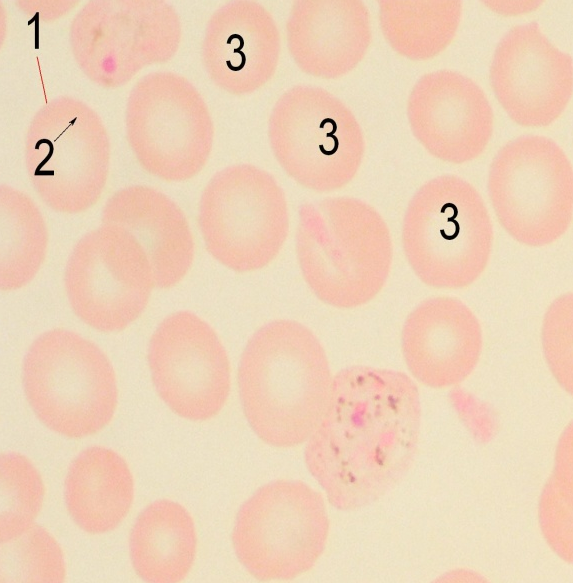
| 1- 2- 3- |
Large magnification
4. Consider the microslide "Fat inclusions in the cells of the axolotl" with small and large magnification. Draw and designate the structure of the animal cell with lipid inclusions.
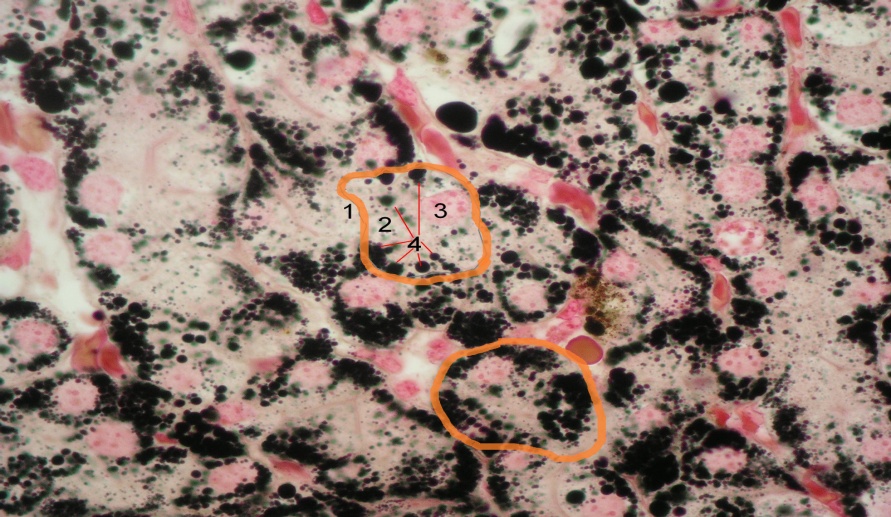
| 1- 2- 3- 4- |
Large magnification
5. To consider the micropreparation "Pigment inclusions in the skin of the tadpole" with small and large magnification. Draw and designate the structure of the animal cell with pigment granules.
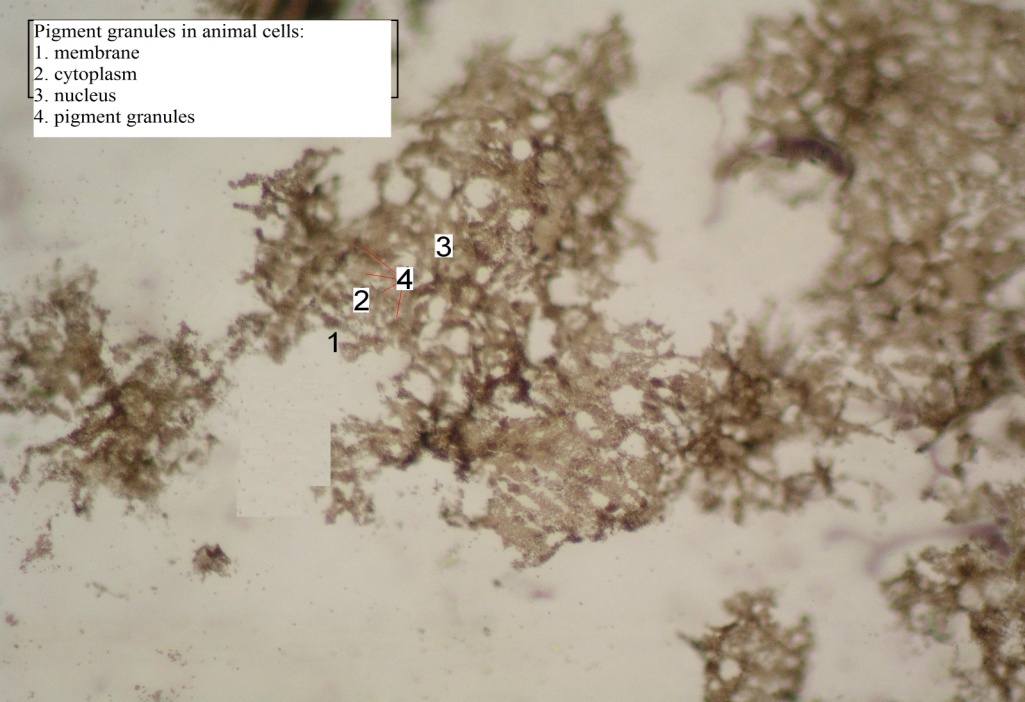

| 1- 2- 3- 4- |
Large magnification
6. Write the differences between the animal and plant cells.
| a characteristic | Plant cell | Animal Cell |
| Plastids | ||
| Method of nutrition | ||
| Synthesis of ATP | ||
| ATP cleavage | ||
| Сentriole | ||
| Cellulose Cell Wall | ||
| Inclusions |
7. Draw a diagram of the structure of animal and plant cells, note the details of their structure. 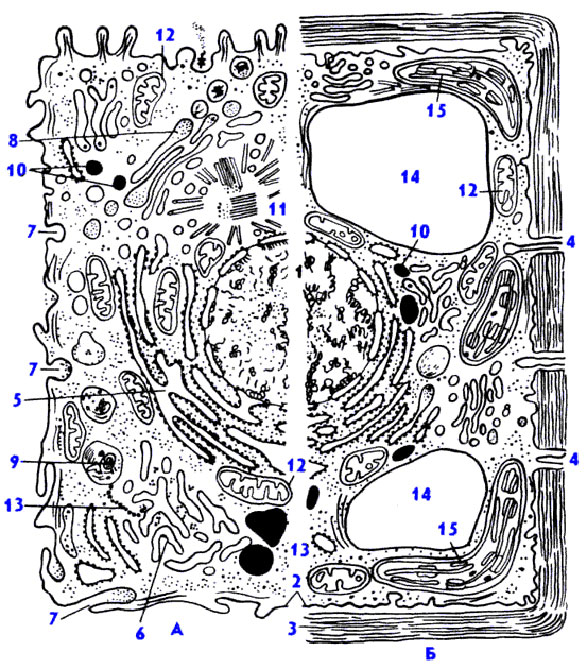
An animal cell; plant cell; nucleus with chromatin and nucleolus; the plasma membrane; cell wall; plasmodesma; granular cytoplasmic reticulum; smooth reticulum; pinocytosis vacuole; Golgi apparatus; lysosome; fatty inclusions in the smooth reticulum; centriole and microtubules of centrospheres; mitochondria; polylibosomes of the hyaloplasm; central vacuole; chloroplast.
8. Study the structure of the cell membrane and designate the pattern.
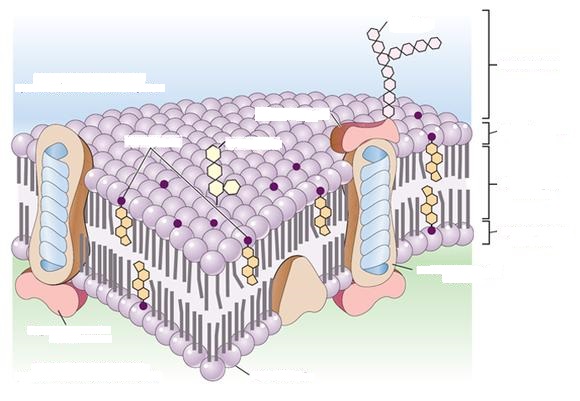
The structure of the cell membrane: the outer surface of the cytoplasmic membrane, carbohydrate, glycoprotein, glycolipid, cholesterol, glycocalyx, hydrophilic region, hydrophobic region, integrated protein, phospholipid, peripheral protein, inner surface of the cytoplasmic membrane.
9. Consider osmotic processes in the plant cell.
• Turgor. Prepare a temporary preparation of onion film cells in a drop of water (isotonic medium); Observe the turgor state of cells with a large magnification of the microscope.
• Plasmolysis. Prepare a temporary preparation of onion cells in a drop of 10% NaCl solution (hypertonic medium). Observe at high magnification gradual flaking of the cytoplasm from the membrane and compaction of the protoplast is a phenomenon of plasmolysis.
• Deplasmolysis. Plasma cells are washed with water, the preparation is again prepared in a drop of distilled water (hypotonic medium) and with ultrasonic waves. 7x40 to observe the phenomenon of deplasmolysis.
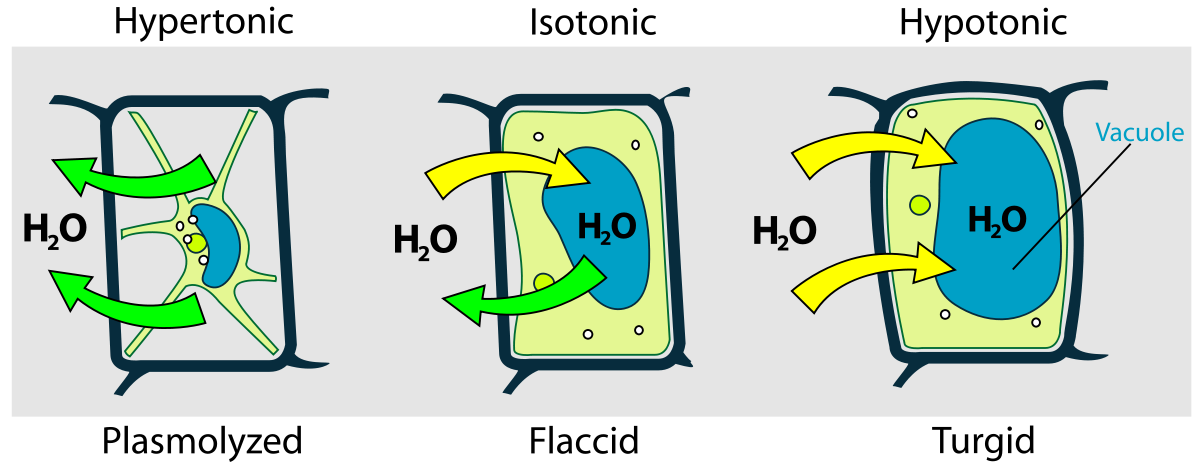
Draw a human erythrocyte, designate the cell membrane and protoplast.
а) b) с)
Human erythrocyte in: a) isotonic medium (water) - turgor; b) hypertonic medium (10% of r-p NaCl) - plasmolysis; c) hypotonic environment (distilled water) - deplasmolysis.
10. To view and identify the processes of transport of substances through the membrane. 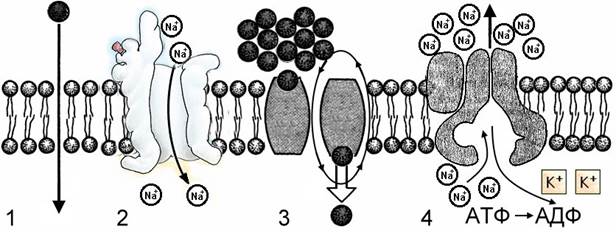
_____- simple diffusion;
_____- diffusion through membrane channels;
_____-facilitated diffusion with carrier proteins;
_____- active transport
Teacher's signature ______________________________________
Date: Practical lesson №3.
Дата добавления: 2020-11-15; просмотров: 440; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
